(Stephen’s favorite colors are dark green, fire orange, and plum purple)
Plants are living organisms just like us. They need certain things to survive and if you manage these things properly your plants will thrive.
Light
Plants need light. Light is the catalyst that plants need to create usable energy through photosynthesis. Plants catch light with something called chlorophyll. Plants prefer sunshine, but you can use a grow light for growing indoors or underground.
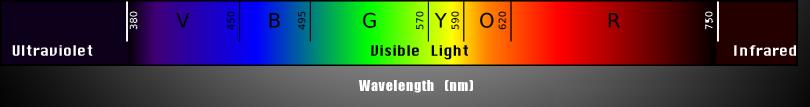
Plants use the spectrums between 390-480 nm and 620-700 nm.
The duration and quality of the light are important. Light is qualified by it’s different spectrums or wave lengths. The human eye can see the wave length light spectrum between about 390 nm to about 750 nm. Chlorophyll is most productive with the spectrum between 390 nm and 480 nm or the “blues” and the spectrum between 620 nm and 700 nm or the “reds.” Most of the spectrum between 480 nm and 620 nm is reflected back. This is the referred to as the “greens” and is the reason plants are green.
Different colored light also affects the plants differently. Blue light helps with vegetative leaf growth, while, red light, when combined with blue, allows plants to flower.
The energy provided by light helps plants fight off pests, recover from extreme weather or disease, and reproduce. Most garden plants need at least 6 hours of sun, but some, like tomatoes, prefer 10 or more. It is also important to have a period of darkness so the plants can rest.
Air
 Like us, plants need to breath, but unlike us they use different things from the air than we do. The Earth’s atmosphere is primarily made of oxygen (O2), Nitrogen (N2), and Carbon Dioxide (CO2).
Like us, plants need to breath, but unlike us they use different things from the air than we do. The Earth’s atmosphere is primarily made of oxygen (O2), Nitrogen (N2), and Carbon Dioxide (CO2).
Plants use CO2 during photosynthesis to make simple sugars like Photosynthate. During this process the plant takes the Hydrogen from Water (H2O) and combines it with the Carbon in CO2 to make these sugars and releases Oxygen as O2 into the atmosphere.
In order to break down these sugars for energy the plants need Oxygen. This process is called respiration. A plant’s roots also need Oxygen; this is why your soil is very important. If your plant is yellowing, it could mean that the roots are not getting enough Oxygen. This could be caused from compact soil, or over watering.
Soil
Soil provides a medium for the plant to grow in. It anchors the plant and provides the plants roots with access to water and nutrients. Plants grown in hydroponics will need to have some kind of artificial support and nutrients added to the water.
 Soil is a living thing. It is important to cover it with mulch. Like our skin, the mulch will protect the soil, keep it moist, regulate its temperature and prevent compaction. It is important for your soil to be loose or fluffy. Compact soil makes it difficult for plant roots to spread out, which limits their access to Oxygen and other nutrients.
Soil is a living thing. It is important to cover it with mulch. Like our skin, the mulch will protect the soil, keep it moist, regulate its temperature and prevent compaction. It is important for your soil to be loose or fluffy. Compact soil makes it difficult for plant roots to spread out, which limits their access to Oxygen and other nutrients.
Nutrients
The most important nutrients for plant growth are Nitrogen (N), Potassium (K), and Phosphorus (P). These are the three numbers you see listed on commercial fertilizers (example 10-10-10). The numbers represent the amount of Nitrogen, Potassium and Phosphorus per pound of fertilizer.
Secondarily plants need Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), and Sulfur (S). In addition, they need small amounts of Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), Boron (B), Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Molybdenum (Mo), and Chlorine (Cl). The best way to make sure your plants have what they need is add organic material to your soil with natural compost, manures, and mulches.
Water
 Water is the life blood of a plant. It moves through the vascular system of the plant, carrying nutrients to the cells of the plant. Xylem vessels take water and nutrients up from the roots to the leaves. Phloem vessels carry sugars and nutrients down or up to different parts of the plant.
Water is the life blood of a plant. It moves through the vascular system of the plant, carrying nutrients to the cells of the plant. Xylem vessels take water and nutrients up from the roots to the leaves. Phloem vessels carry sugars and nutrients down or up to different parts of the plant.
Water helps plants maintain rigidity. Plants cells stay rigid because of turgor pressure, which is caused by a plant cell filling with water and pushing against the cell wall. Wilting, curled and droopy leaves could indicate the plant isn’t getting enough water.
Any excess water is evaporated out of pours in the leaves. However, you can still over water, which can prevent oxygen from getting to the roots, dilute the nutrients and prevent healthy growth.
Temperature
In the spring plants know to start growing because of the temperature of the soil. Most plants look for a temperature of about 55° F. The best time to take the temperature of your soil is early in the morning, because that is when it is the coldest.
Air temperature is also important. Plants grow slower when it is cold and faster when it is warm. Living in the desert, I’ve noticed that some plants stop or slow down their growth when the air temperature gets above the 90° F. Warm-season vegetables like zucchini and okra grow best between 60° and 80° F. Cool-season vegetables like lettuce and spinach grow best between 50° and 70° F.
Space
Over crowding your plants causes competition for nutrients and will stunt their growth. If the roots and foliage don’t have room to grow, it will stress out the plant and prevent healthy growth. Be sure to read the planting instructions of your seed packets for spacing.
Like what you read? Tell a friend by sharing this post on Facebook.
References
http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/light/Lesson-2/Visible-Light-and-the-Eye-s-Response
http://www.aquaticplantcentral.com/forumapc/lighting/38014-lighting-spectrum-photosythesis.html
http://www.life.illinois.edu/govindjee/photosynBook/Chapter2.pdf
http://www.botany.uwc.ac.za/ecotree/photosynthesis/spectrum.htm
http://www.aces.uiuc.edu/vista/html_pubs/hydro/require.html
http://www.gardeningknowhow.com/special/children/how-plants-grow.htm
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yzn-Hqd-p88
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e9XsjCp62dY
http://www.nysipm.cornell.edu/teaching_ipm/sole/green_sci/plants_need.pdf
http://www.ncagr.gov/cyber/kidswrld/plant/label.htm
https://sensing.konicaminolta.us/blog/can-colored-lights-affect-how-plants-grow/



How do you make compost
Great question Lisa. I’ll start with how I make compost and then give you some general guidelines.
First, compost is simply decayed organic material. This means any plant or food waste as well as wood and paper products can be turned into compost. So everything from an old cotton t-shirt to a banana peel can be turned into compost.
I make compost by throwing all of my food waste except a few items (see list below) into a 5 gallon bucket in my kitchen. I keep a lid on it to reduce smell. Once the bucket if full, I dump it into a pile I have in a bin in the corner of my yard. After I dump out the bucket, I use a shovel to fold my compost over covering up the newly added refuse. Finally I rinse out the bucket with a hose and wet down the compost.
The best time to start a compost pile is in the fall, because you usually have some fallen leaves to start your pile with. You can also shred up your garden plants as the cold kills them. If you want to start one now, just toss your bucket of refuse on the ground and sprinkle about 1/2 of dirt on it to cover it up. As you fold in more buckets, you may need to add some dirt on top, but eventually you will have enough compost to do the trick.
Mold and bacteria will find and break down your compost for you. All you need to do is keep it damp and aerated. The molds and bacteria need water and oxygen to break down the organic material.
Here are some things I add
Left over starches like rice or pasta, vegetable table scraps, egg shells, apple cores, banana peels, cooking scraps, napkins, and old breads.
Here are items I exclude: meat, bones, milk, lemon and other citrus peels. I also don’t compost drier lint, paper, or cardboard. (I do compost shredded paper and you could compost cardboard, but I would suggest you shred it first.)
I don’t worry about this next part too much, but for best results, you want to try and balance the amount of wet/green material with the amount of dry/brown material. The rule of thumb is equal parts by weight. Greens are things like vegetable scraps or grass clipping, browns are things like breads, dry leaves and straw.
Good luck! And let me know how it turns out.